解答
結合 Eqs. 10.2-14 和 10.2-1 可得
若長度為 L,則電流密度 I (electrical density) 與電壓降 E (voltage drop) 的關係為
因此
從上式可得知
對於銅,在 §9.5 的 Lorenz 數是 k/keT0 = 2.23 ×10-8 volt2/K2。因此,造成 10℃ 溫度上升需要的電壓降為
Reference: RB Bird, WE Stewart, EN Lightfoot, Transport Phenomena, 2nd ed (Wiley 2002).




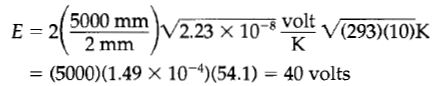
沒有留言:
張貼留言