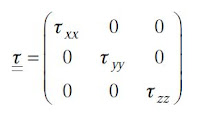這裡我們檢驗一下共旋馬克斯威爾模型 (corotational Maxwell model) 於簡單剪切流場 (simple shear flow) 的預測。Corotational Maxwell 模型是線性黏彈性 Maxwell 模型之延伸,可視為非線性黏彈性的模型 (nonlinear viscoelastic model)。Maxwell 模型為
 (1)
(1)
而 corotational Maxwell 模型為
 (2)
(2)
Equations 1 與 2 唯一的差別是前者為時間偏微導數 (partial time derivative),後者為共旋時間導數 (corotational time derivative)。相較於時間偏微導數,共旋時間導數的引入將滿足客觀性原則 (principle of objectivity),即應力張量的表示將與流體單元在空間中的瞬間方向性無關 (the expression for the stress tensor should be independent of the instantaneous orientation of a fluid element in space)。在 Eq. 2 中,剪切應力張量 τ 的共旋時間導數為 τ(0) (= Dτ/Dt),即
 (3)
(3)
其中,D/
Dt 為時間實質導數 (substantial derivative)。於簡單剪切流場,速度梯度張量 (velocity gradient tensor) 為
 (4)
(4)
渦度張量 (vorticity tensor) 為 ω = ▽∙u - (▽∙u)T
 (5)
(5)
應力張量 (stress tensor) 為
 (6)
(6)
速度向量的各分量為
 (7)
(7)
應變率張量為 (rate-of-strain tensor or rate-of-deformation tensor)
 (8)
(8)
結合 Eqs. 2 至 7,以及應力張量不隨位置和時間而變的假設 (即 Eq. 3 的第一項時間實質導數 為零 Dτ/Dt = ¶τ/¶t + ux¶τ/¶x + uy¶τ/¶y + uz¶τ/¶z = 0,但第二項 1/2{ω ∙ τ - τ ∙ ω} 不為零),我們可得以下結果,黏度與剪切率的相依性為
 (9)
(9)
Figure 5.27 為黏度對剪切率的作圖,相同於 Maxwell 模型,corotational Maxwell 模型預測了牛頓平台區 (Newtonian plateau),但後者模型更成功預測實驗上常見的剪切致稀的行為 (shear thinning)。當 λ0 越大,剪切致稀將提前在低剪切率發生。另外,此模型對第一正向力差值 N1 (first normal stress difference) 和其係數 ψ1 (正值) 之預測為
 (10)
(10)
第一和第二正向力差值係數之理論比值為 (ψ2 負值)
 (11)
(11)
實驗上,第二正向力差值較第一正向力差值難以測得,因此常以下式近似之
 (12)
(12)
同時,Eqs. 10 和 11 告訴我們,corotational Maxwell 模型預測的第一和第二正向力差值異號且不為零。Figure 5.28 是第一正向力差值係數對剪切率的作圖,隨著剪切率越大,正向力差值係數越小。
雖然 corotational Maxwell 模型錯誤預測程度過大的剪切致稀行為 (excessive shear thinning;即在剪切率為 1/λ0 1/s 時,Equation 9 預測應力將有最大值) 和過大的正向力差比值 (實驗值約 - 0.1 至 - 0.4,而非 - 0.5),但是僅有兩個參數的 corotational Maxwell 模型 (λ0 和 η0), 已可定性補捉低剪切率之流動行為,並幫助我們學習處理更進階的非線性黏彈模型。
 |
Figure 5.27 Corotational Maxwell 模型對黏度之預測
|
 |
同 Figure 5.27
|
 |
Figure 5.28 Corotational Maxwell 模型對第一正向力差值係數之預測
|
 |
| 同 Figure 5.28 |
Reference: T Osswald and N Rudolph, Polymer Rheology: Fundamentals and Applications (Hanser 2015).

 (7)
(7)